Summary
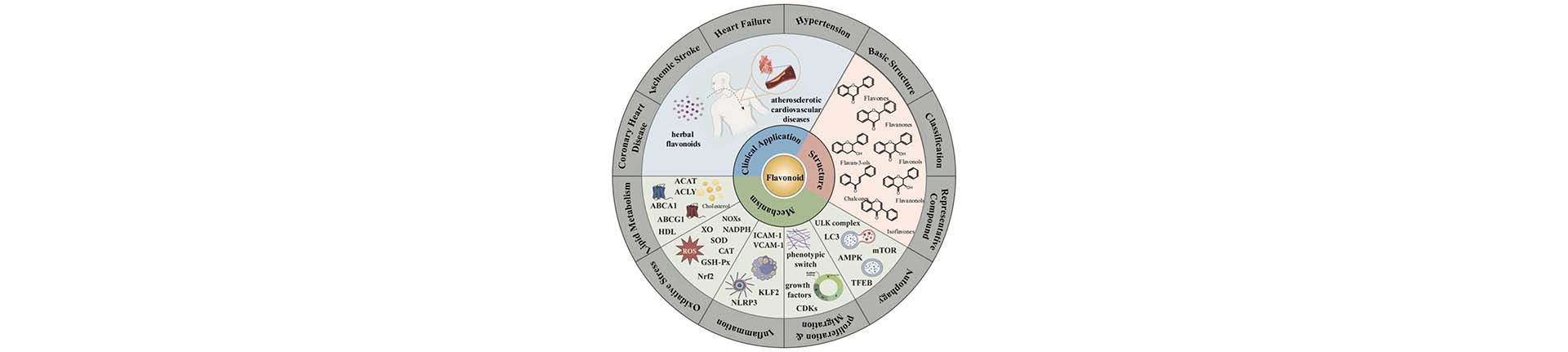
The review summarizes how flavonoids derived from herbal medicines help combat atherosclerosis (AS), a leading cause of cardiovascular diseases. The authors outline how flavonoids regulate lipid metabolism, counter oxidative stress, suppress inflammation, inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and activate autophagy—key mechanisms implicated in AS development.
The review highlights various subclasses of flavonoids, such as flavones, flavonols, isoflavones, and biflavonoids, detailing their structural features and biological effects. Additionally, the paper discusses specific molecular pathways regulated by flavonoids, and clinical findings that support the therapeutic potential of flavonoids in managing AS.
Overall, it positions herbal flavonoids as promising candidates for safer and more comprehensive treatment strategies against atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
M. Huang et al., “The multifaceted anti-atherosclerotic properties of herbal flavonoids: A comprehensive review,” Pharmacological Research, vol. 211, p. 107551, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107551.